Signalment:
Juvenile, female, Mahogany,
Mustela vison, minkFarmed mink from a ranch with 9700 kits are experiencing reduced feed intake, increased mortality in this seasons juveniles (averaging 10 deaths per week, recently up to 10 deaths per day). This ranch was cleaned and restocked 1.5 years ago. Kits are vaccinated with a four-way vaccine (against botulism, distemper, mink enteritis virus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) at 10 weeks of age; no Aleutian disease testing has been done since restocking.
Gross Description:
This female mink exhibited pulmonary congestion and edema, splenic enlargement and an empty gastrointestinal tract on gross postmortem.
Histopathologic Description:
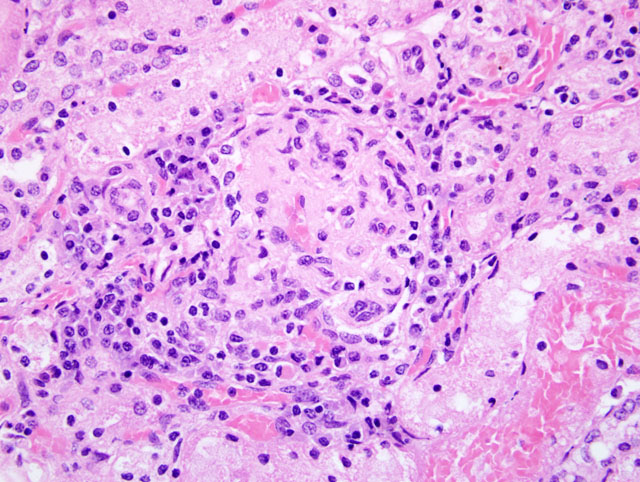
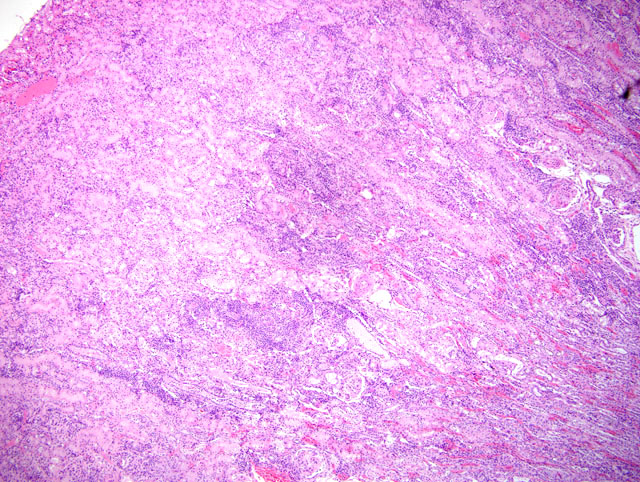
Kidney: Glomeruli throughout the section exhibit a variety of lesions, including increased cellularity of the glomerular tuft with segmental to diffuse mesangial hyperplasia and hyalinization, and thickened glomerular basement membranes and Bowmans capsules (
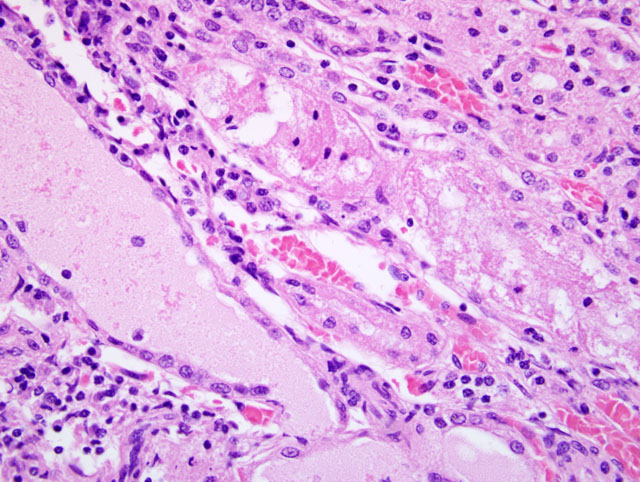
Fig. 2-1). Some glomeruli are obsolescent. There are prominent interstitial infiltrates of plasma cells and lymphocytes, with associated tubular degeneration(
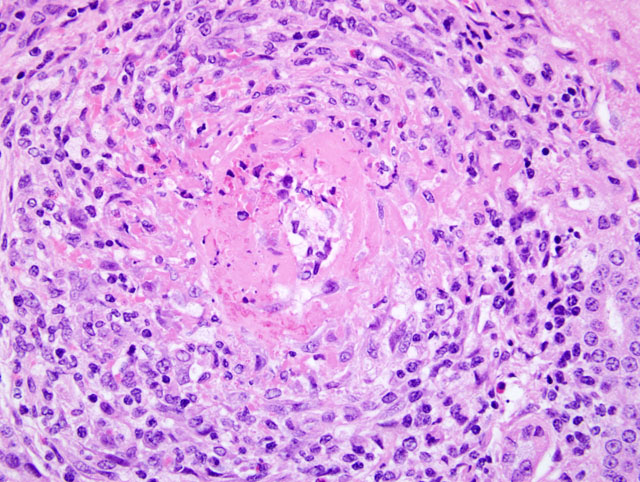
Fig. 2-2, 2-3). Many tubules contain protein or cellular casts. Occasional small to medium-sized arterioles display fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls, with infiltrating inflammatory cells and cuffs of mixed inflammatory cells (
Fig. 2-4).
Urinary bladder: Arteries within the muscular wall and adjacent mesentery are surrounded by thick concentric cuffs of mixed inflammatory cells, including macrophages, plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils. There is fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel walls, some with infiltrating inflammatory cells.
Morphologic Diagnosis:
Generalized, segmental to diffuse glomerulonephritis
Interstitial nephritis
Necrotizing arteritis, kidney, urinary bladder
Lab Results:
Seven of eight serum samples submitted tested POSITIVE for Aleutian disease parvovirus antibodies by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE).
Spleen tissue from this mink tested positive for Aleutian disease parvovirus by PCR.
Condition:
Aleutian mink disease
Contributor Comment:
The histologic lesions in this case are compatible with Aleutian disease. This diagnosis is supported by the positive serology testing and confirmed by PCR. Aleutian disease, a chronic progressive disease of mink caused by the Aleutian disease parvovirus, is considered the most important disease affecting mink production worldwide, causing increased early kit mortality and chronic disease with high mortality in juveniles and adults.(3) Disease severity and development of lesions is dependent on the age and genetics of the mink, and the virulence of the strain of infecting virus.(2) While kits succumb to interstitial pneumonia and respiratory failure, the chronic form of the disease is result of immune complex glomerulonephritis and vasculitis, and death is usually a result of renal failure. The humoral immune response plays a direct role in the pathogenesis of Aleutian disease.(1) Antiviral antibody can be detected as early as five days post-infection, with development of a marked, progressive polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia. While antibody can have a partially protective role via viral neutralization and incomplete restriction of virus replication in ACV-infected mink kits, it does not prevent infection. In older animals, antiviral antibody is thought to exacerbate disease through a variety of mechanisms, including antibody-dependent enhancement of infection (where antibody bound to virus facilitates viral entry into macrophages via Fc receptors; Fc receptor binding stimulates IL-10 production, which inhibits interferon signaling, promotes antibody production and suppresses cytotoxic T-cell-mediated killing of virus-infected cells), and formation and tissue deposition of immune complexes, with subsequent development of immune-complex vasculitis and glomerulonephritis.
JPC Diagnosis:
Kidney: Glomerulonephritis, membranoproliferative and necrotizing, diffuse, moderate with multifocal necrotizing arteriolitis, subacute interstitial nephritis, and rare protein casts
Conference Comment:
Aleutian disease was first reported in 1956 in Aleutian mink homozygous for the gene that is responsible for their steel- blue color. Mink and ferrets are susceptible to Aleutian mink disease (ADV). Genetic susceptibility plays a major role in ADV infections. Mink homozygous for the autosomal recessive Aleutian gene are more severely affected by ADV often resulting in death. ADV can cause disease in other types of mink ranging from death to subclinical infection.(2)
During the conference discussion Dr. Williams stated that the lesions in this case were quite striking and more severe than most cases of ADV he has seen. As the contributor mentioned, kits get an interstitial pneumonia, and type II pneumocytes are the primary site of replication leading to death of infected cells and a fulminant pneumonia with death. Rarely intranuclear inclusions are found in pneumocytes, and severe cases of pneumonia can lead to alveolar hyaline membrane formation.(1) Infection of adults leads to an insidious chronic form with splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, hypergammaglobulinemia, and acute interstitial nephritis.(1) Chronic disease causes death via uremia and kidney failure.(3)
Gross lesions in the chronic form include ulceration of the mouth, tongue, footpad, and stomach secondary to uremia.(3) Histologic lesions in the chronic form are impressive and consist of lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis, marked glomerulonephritis, and a necrotizing vasculitis of the small and medium sized arteries.(3)
References:
1. Best, SM, Bloom, ME: Pathogenesis of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus and similarities to B19 infection. J Vet Med B
52:331-334, 2005
2. Hadlow WJ, Race RE, Kennedy RC: Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect Immun
41:1016-1023, 1983
3. Hunter DV: Aleutian Disease.Â
In: Mink biology, health and disease, eds. Hunter DB, Lemieux N, pp. 8-21 8-26. University of Guelph, ON, 1996