JPC SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
August 2024
D-B01
Signalment (JPC #1104736): Guinea pig
HISTORY: None
HISTOPATHOLOGIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Affecting approximately 10% of the hepatic parenchyma are multifocal, random, variably sized (up to 1.5mm diameter) necrotic foci characterized often by both coagulative and lytic necrosis, with retention of cellular architecture with loss of differential staining or eosinophilic cellular and karyorrhectic debris, respectively. Necrotic foci are surrounded and infiltrated by neutrophils, lymphocytes, and macrophages (paratyphoid nodules) and contain variable amounts of fibrin and hemorrhage. Hepatocytes adjacent to necrotic foci are often swollen with pale, vacuolated cytoplasm (degeneration). Periportal connective tissue is multifocally infiltrated by low to moderate numbers of lymphocytes, plasma cells, fewer neutrophils, and macrophages. There is a mild increase in the number of biliary ductular profiles (ductular reaction) and lymphatics are multifocally ectatic. Remaining less affected hepatocytes are often expanded by one to few clear cytoplasmic vacuoles up to 12µm in diameter that displace the nucleus (vacuolar change, lipid-type). Multifocally the capsule is irregular and expanded up to two times normal by variable numbers of neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages.
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, neutrophilic and lymphohistiocytic, multifocal, random, moderate, with mild ductular reaction and moderate lipid-type vacuolar change, guinea pig (Cavia porcellus), rodent.
ETIOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Hepatic salmonellosis
CAUSE: Salmonella Enteritidis
GENERAL DISCUSSION:
- Salmonella spp are gram-negative, aerobic to facultatively anaerobic, motile bacteria (Enterobacteriaceae family) that have a broad host range and cause important nosocomial and zoonotic infections
- Taxonomy is currently based on molecular genetic analysis: the genus Salmonella is divided into two species: S. bongori and S. enterica; there are 6 subspecies of S. enterica (enterica, salamae, arizonae, diarizonae, indica, houtenae) and many (>2,500) serovars/serotypes, 60% of which belong to S. enterica subsp. enterica
- Nomenclature: Names of serotypes are capitalized and not italicized (e.g. Salmonella enterica subsp enterica serotype Typhimurium is shortened to Salmonella Typhimurium)
- Members of S. e. enterica are the predominant cause of salmonellosis in humans and domestic animals; the remainder are found in ectothermic animals or the environment
- Highly host-adapted serotypes tend to produce severe systemic disease in all ages of animal (e.g. S. Dublin in cattle, S. Choleraesuis in swine) and are more likely to produce a carrier state in host animals, while serotypes with a broad host range (e.g. S. Typhimurium) tend to affect predominantly young animals in most species and mainly cause enterocolitis (although septicemia may occur); those serotypes that invade systemically have the ability to survive and replicate within macrophages
- Asymptomatic carriage of Salmonella may be common, and this carrier state is important in the epidemiology of the disease
- In guinea pigs, salmonellosis was once very common but is now rare in laboratory animals, but continues to cause disease in pets that are fed contaminated greens; the most commonly reported serotypes are S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis; carrier states may occur
PATHOGENESIS:
- In domestic animals, transmission can occur directly or indirectly (contamination of feed, water, or the environment) by ingestion or less commonly inhalation; in guinea pigs, ingestion is most common but the conjunctiva has also been shown to be an important portal of entry
- The disease form that develops (septicemic, acute enteric, or chronic enteric) depends on the challenge dose of bacteria, previous exposure, and stress factors
- Stressors and/or diseases that compromise immune competence or disrupt the enteric bacterial ecosystem are often implicated in salmonellosis
- Ingestion (fecal-oral) à mucosal colonization via either M cells or enterocytes depending on species (Salmonella spp. are motile, using flagella) à attachment to the surface (colonization) via ligand-receptor interaction (likely involving specific fimbriae) à invasion of enterocyte via type III secretion system (T3SS) that stimulates target cell actin filament mobilization and phagocytosis à bacterial survival within Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV) à host production of inflammatory mediators (e.g. PGE2) à enterocolitis and hypersecretion of chloride with resultant passive osmotic movement of water into intestinal lumen and enterocyte death à reduced absorptive area of intestinal villi as well as defects in mucosal integrity à leakage of proteinaceous and neutrophil-rich exudate into lumen (may contain sufficient fibrinogen to form a pseudomembrane) à bacterial spread via leukocyte trafficking via the portal vein to the liver forming foci of bacterial and toxin-mediated necrosis and inflammation (paratyphoid nodules) +/- bacteremia if the bacteria is capable of surviving and replicating within macrophages (i.e. leukocyte trafficking) à major immune response elicited via pattern recognition receptors (e.g. toll-like receptors)
- The mechanism of injury is acute coagulative necrosis to cells caused by bacterial toxins and by acute inflammation and its mediators and degradative enzymes, with injury of the vascular system including vasculitis and thrombosis caused by bacterial toxins
- Neutrophilic influx is associated with upregulation of CXC chemokines (IL-8, growth-related oncogene-α (GRO-α), granulocyte chemotactic protein-2 (GCP-2)), IL-1β, IL-1 receptor-α (IL-1Rα), and IL-4
- Colonization of mesenteric lymph nodes and gallbladder may result in inapparent carrier state
- Virulence factors: The ability to attach, invade, and penetrate enterocytes is crucial to virulence and is the first step in the development of salmonellosis; virulence factors are often encoded in chromosomes in clusters of genes (pathogenicity islands [PAI]) known as Salmonella pathogenicity islands (SPI) (there are at least 21 SPIs, with most attention paid to SPI-1 and SPI-2), and also in bacteriophages and plasmids
- SPI-1:
- Encodes type III protein secretion system-1 (T3SS-1) required for invasion of nonphagocytic cells
- Effector proteins induce secretory diarrhea by blocking chloride channel closure (diarrhea is NOT mediated by enterotoxins like with E. coli and cholera), attract neutrophils (via activating NFkB and activator protein-1 à release of IL-8 à neutrophil chemotaxis), and induce enterocyte apoptosis à diarrhea due to active electrolyte secretion, malabsorption due to reduced mucosal surface area and enterocyte competence, and inflammatory exudation
- SPI-2:
- Genes are activated in the phagosome (SCV)
- Encodes T3SS-2 effectors that allow for survival and replication within macrophages in SCV (in host-adapted strains), perhaps largely through inhibition of NADPH oxidase
- Motility associated with the presence of flagella may enhance movement through the glycocalyx and facilitate attachment to specific receptors on enterocytes
- Pili or fimbriae may play a role in attachment
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Salmonella with smooth cell walls (most of those isolated from animals) has an O-specific side chain, a core portion, and a lipid A portion which allow the bacteria to be more invasive, more successful at avoiding phagocytosis, and assist in lysis of phagolysosomes after invasion; some pathogenic strains do not require intact LPS for invasion but host-adapted serovars do; the lipid A portion is responsible for the endotoxin-mediated effects e.g. thrombosis of mucosal venules which is common
- Effector proteins that modify the metabolism or cause death of host cells, e.g. type I secretion system can kill macrophages via apoptosis leading to activation of caspase-1
TYPICAL CLINICAL FINDINGS:
- In domestic animals, syndromes vary from localized enterocolitis to septicemia; abortion may occur with or without obvious systemic disease
- Salmonellosis is more common and more severe in young animals, and young animals are more likely to succumb to septicemia
- Septicemia may be of variable duration and severity but is often rapidly fatal
- In guinea pigs:
- Clinical signs are often nonspecific and include depression, lethargy, dyspnea, peracute death often without diarrhea, abortions
- In chronic disease, signs include anorexia and weight loss, conjunctivitis, rough hair coat, small litters, and sporadic death
- All ages and strains are susceptible, but young weanlings and sows around farrowing time are particularly at risk
- Mortality is typically around 50% but can reach 100%
TYPICAL GROSS FINDINGS:
- Gross lesions of guinea pigs are similar to those in other mammals and include: pinpoint to several millimeter diameter pale foci of the liver and spleen (paratyphoid nodules) +/- other organs (lung, pleura, peritoneum, uterus), enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes, splenomegaly; lesions may be absent in peracute cases
- In general across species, there are three forms of salmonellosis:
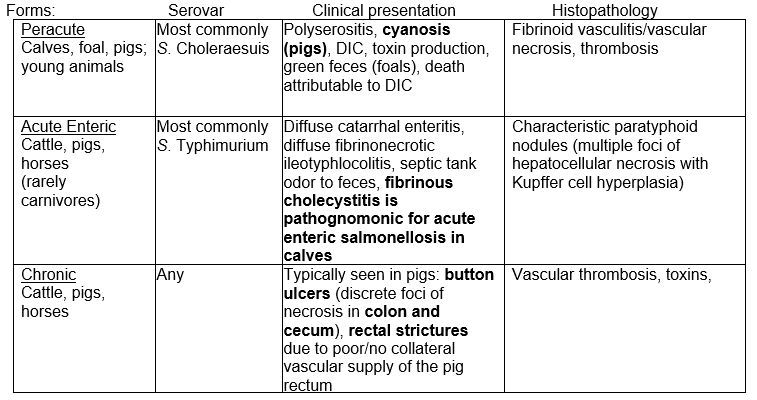
TYPICAL LIGHT MICROSCOPIC FINDINGS:
- Liver: Characteristic paratyphoid nodules may be found in all transitional stages from foci of nonspecific necrosis to reactive granulomas depending on duration; the initial change is focal coagulative necrosis, then macrophages accumulate around the margin and expand and displace parenchymal cords (some references refer to this as Kupffer cell hyperplasia); these may also be found in the spleen and/or lymph nodes
- Enteritis: Fibrinous to fibrinohemorrhagic exudates over denuded small and large intestinal mucosae; suppurative inflammation may occur in lymphoid tissues of the intestinal tract (GALT)
- Fibrinonecrotic ileotyphlocolitis
ADDITIONAL DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:
- Definitive diagnosis requires culture or molecular confirmation
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
Hepatic necrosis in a guinea pig:
- Clostridial enterotoxemia (C. perfringens, C. difficile): Acute fatal necrotizing typhlitis
- Yersiniosis (Y. pseudotuberculosis): Large colonies of bacteria
- Tyzzer’s disease (Clostridium piliforme): Portal necrosis; focal to segmental cecal mucosal necrosis; characteristic intracellular bacteria (Warthin-Starry or Giemsa)
- Pneumococcal septicemia (Streptococcus pneumoniae): Acute fibrinous bronchopneumonia, pleuritis, pericarditis, peritonitis, consolidated lung lobes
COMPARATIVE PATHOLOGY:
- Bacterial multifocal hepatic necrosis affecting multiple species: Listeria monocytogenes (fetal and neonatal lambs, calves, foals, piglets), Actinobacillus equuli (foals), Actinobacillus suis (pigs), Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (lambs, occasionally dogs and cats), Francisella tularensis (lambs, cats), Mannheimia haemolytica and Histophilus somni (lambs), Salmonella (all hosts), Clostridium piliforme (Tyzzer’s disease; foals, dogs), Nocardia asteroides (dogs), mycobacteria (all hosts)
Swine:
- Many serotypes have been isolated (S. cholerasuis and S. typhimurium most common), and swine serve as an important reservoir of Salmonella along with poultry and cattle; carrier swine harbor the bacteria in the intestinal lamina propria and regional lymph nodes therefore bacteria are not necessarily shed in feces
- There is a strong association between Classical swine fever virus (Pestivirus, formerly known as hog cholera) and S. Choleraesuis, as S. Choleraesuis can be recovered from 10-50% of swine with CSF infection
- Domestic swine have 3 syndromes:
- 1. Septicemic salmonellosis:
- Affects both young and adult pigs and is usually fatal
- Usually associated with host-adapted S. Choleraesuis var. kunzendorf
- Septicemia and enteritis usually occur separately, septicemia is more common
- Acute enterocolitis can result in large necroulcerative lesions in the colonic mucosa (button ulcers)
- Systemic lesions: Interstitial pneumonia (dyspnea), cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin especially tail, snout, and ears is characteristic but not pathognomonic), less commonly multifocal petechiae (especially laryngeal mucosa), hemorrhagic lymph nodes, splenomegaly, congested liver with focal to large hemorrhages +/- tiny yellow foci of necrosis (paratyphoid nodules), pinpoint renal hemorrhages (“turkey egg kidney”), red-black stomach with fibrinonecrotic to sloughed mucosa, catarrhal to hemorrhagic enteritis, and occasionally polyarthritis; (Savic et. al 2021)
- Histologic changes are associated with endothelial damage from endotoxin and focal localization of bacteria
- 2. Enterocolitis:
- Disease of feeder pigs with high morbidity but low mortality; may remain carriers with S. Typhimurium persistence in mesenteric lymph nodes and persistent shedding (Bellido-Carreras et. al., 2019)
- Usually associated with S. Typhimurium, though a recent article cited S. enterica ssp. Enterica serovar 4, [5],12: i:- as the primary serovar (Naberhaus et. al. 2019)
- Acute or chronic disease including ischemic necrotizing proctatitis which may lead to rectal stricture due to poor/no collateral vascular supply of the pig rectum with resultant proximal colon dilation; disease is a fibrinous, erosive to focally ulcerative (diphtheritic membrane) condition mainly of the cecum, colon, and rectum but occasionally the distal small intestine; intestinal content is fluidic but not usually bloody, and mesenteric lymph nodes are prominent
- Button ulcers are NOT associated with this or other non-host-adapted serovar
- Typhlocolitis differential diagnosis: Swine dysentery (Brachyspira hyodysenteriae), other spirochetoses, Salmonella enterocolitis, Lawsonia intracellularis
- 3. Ulcerative enterocolitis:
- Uncommon condition of 2-4 month old pigs
- Caused by S. Typhisuis
- Other lesions include caseous tonsillitis, lymphadenitis, and suppurative parotid sialoadenitis resulting in massive enlargement of the neck
- May cause button ulcers of the ileum, cecum, colon, and rectum
- Wild suids are worldwide often asymptomatic reservoirs for Salmonella spp.
- Symptomatic individuals often have necrohemorrhagic enterocolitis with button ulcers in the cecum and colon, also liver and pericardial hemorrhages, splenomegaly; S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium have been isolated
Horses
- S. Typhimurium serovar most common, increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant definitive phage type 104 (DT104); antibiotic resistance associated with the presence of resistance (R) plasmids that may be transferred between different species of bacteria via conjugation or transduction
- Many horses are carriers, and develop diarrhea following stress; treatment with antibiotics is also a predisposing factor to developing diarrhea
- Clinically, salmonellosis may manifest as:
- Septicemia: Peracute/acute in foals 1-6 months old, tends to be fatal, develop diarrhea with a characteristic green color, and those that survive beyond a week may develop pneumonia, osteitis, polyarthritis, and meningoencephalitis
- Enteric form: Acute to chronic in older horses, occurs 2-4 days following stress; acute to chronic enteritis or acute colitis/typhlocolitis (differentials include intestinal clostridiosis and Potomac horse fever); diarrhea is the main clinical sign; the longer the disease course, the lower in the intestine are the most severe lesions, and lesions may be subtle in chronic enteric salmonellosis; histologically, inflammatory infiltrate is largely mononuclear, and fibrin thrombi are frequently present in capillaries or venules of the lamina propria
- Asymptomatic carrier state
- Enteric salmonellosis can cause secondary fungal pneumonia (Hensel et al. 2020)
- S. Abortusequi is a pathogen restricted to horses and has been associated with abortion and neonatal septicemia and polyarthritis commonly in Africa and Asia and sporadically elsewhere
- Recent report of an outbreak causing high mortality in neonatal foals with apparently uninfected dams in a herd in Italy (Grandolfo et. al. 2018)
- S. Infantum has been associated with disseminated infection
Cattle
- S. Typhimurium and S. Dublin (host-adapted, tends to occur in epizootics) are most common, but S. Newport identified as an emerging pathogen; the multidrug-resistant strain S. Typhimurium DT104 is the leading cause of bovine salmonellosis in some parts of the United States
- In calves > 1 week old (< 1 week is more likely to be colibacillosis), acute septicemic febrile disease typified by dejection, dehydration, +/- yellow-grey odiferous diarrhea; morbidity and mortality may be considerable; lesions resemble septicemic colibacillosis but enlargement of mesenteric lymph nodes and gross enteric lesions (usually most severe in the ileum, leaving the duodenum relatively unaffected) are generally observed; characteristic lesions include fibrinous cholecystitis, splenic miliary foci of necrosis or inflammatory nodules, hepatic paratyphoid nodules/granulomas of the liver +/- kidney, lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, interstitial to cranial bronchopneumonia, purulent exudate in synovial cavities, pulmonary alveolar capillary neutrophilia
- A recent paper (Costa et. al 2018) highlights the potential for uropathogenicity (urocystitis and ureteritis) amongst the other systemic manifestations caused by Salmonella Dublin
- In adult cattle, salmonellosis may cause outbreaks as in calves but more commonly causes chronic diarrhea and loss of condition; the source is often carrier animal(s) that may harbor S. Dublin for years/life (vs. other serovars which rarely persist beyond 18 months); abortions are common with S. Dublin but may occur with any serovar and may cause fetal interstitial pneumonia; lesions include fibrinonecrotic (diphtheritic) enteritis, fibrinous cholecystitis, and necrotic Peyer’s patches
- Abortion in cattle has been reported from S. Brandenberg (Siepker et al. 2022)
Sheep
- Uncommon, but outbreaks are always severe and may cause heavy losses; disease findings are similar to those in cattle, including fibrinohemorrhagic enteritis and septicemia
- The most commonly identified serovars are S. Typhimurium, S. Arizonae, and S. enteritidis, and the incidence of S. Dublin is increasing
- Abortion may follow infection by any species of Salmonella (e.g. S. Abortus-ovis, S. Montevideo, S. Brandenburg)
Carnivores
- Salmonella can often be recovered from apparently healthy dogs and cats, but primary disease is rare; characterized by septicemia and gastroenteritis, but conjunctivitis and abortions have been reported in cats
- Raw meat fed to dogs and cats has been shown to have a high incidence of Salmonella contamination which can result in disease including death in cats (Jones et. al. 2019)
- Can occur in association with stress, hospitalization, and antibiotic therapy, and in dogs it can occur secondary to canine distemper and following initiation of chemotherapy in dogs with lymphoma
- S. Dublin has been associated with septicemia in puppies
- Cats in a recent case series had necrotizing enterocolitis, random hepatocellular necrosis and lymphoid necrosis (Riker et al. 2023)
- In felids, fecal culture should be interpreted with caution; in one study, 90% of cats were culture positive for Salmonella spp.
Avian
- The single largest reservoir of Salmonella is domestic poultry; it can cause primary septicemia or noninvasive serotypes may result in a carrier state in birds; most systemic infections are the result of invasion from the gut or extension up the biliary tree
- 4 major diseases caused by Salmonella in poultry: pullorum disease, fowl typhoid, arizonosis, and paratyphoid; caseous cecal cores are strongly suggestive of salmonellosis but are not pathognomonic; disease is rare in commercial operations due to National Poultry Improvement Plan and also recently shown to be rare in backyard poultry in a study in California (Clothier et. al. 2018)
- Pullorum disease and fowl typhoid were previously considered as two distinct diseases caused by S. pullorum and S. gallinarum respectively, but recently the two have been combined under one species, the nonmotile host-adapted Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Pullorum-Gallinarum, with debate as to if they are one or two serovars (see P-B15)
- Pullorum disease: Primarily vertically egg-transmitted disease especially of young chicks and turkey poults characterized by white diarrhea and high mortality in young with asymptomatic carrier adults; now eliminated from commercial poultry operations in the US
- Fowl typhoid: Similar to pullorum disease, but disease often continues for months in chicks/poults, and outbreaks may occur in semimature flocks without history of previous onset; disease in young birds is similar, but disease in semimature birds is characterized by pale head parts (comb, wattles, face), shrunken combs and wattles, and diarrhea; mortality can be substantial
- Arizonosis: Caused by Salmonella Arizonae (see S-B01); egg-transmitted disease characterized by septicemia or localization of infection in the intestine, peritoneal cavity, eye(s) (ophthalmitis is not pathognomonic but suggestive), brain (severe granulomatous ventriculitis), ear (otitis interna) or other sites; mostly affects turkey poults; infection mimics paratyphoid, but previously infected flocks can be identified by birds with atrophied eyes
- Paratyphoid: caused by motile non-host specific S. enterica serovars (e.g. Enteritidis), a public health concern; causes acute or chronic disease in many species of birds and mammals due to effects of endotoxin
- S. Copenhagen causes otitis interna in squabs
- S. Typhimurium is the most common isolate in psittacines and free-living avians; carrier state, can cause hepatosplenomegaly, pneumonia, catarrhal to hemorrhagic enteritis, meningitis, osteoarthritis, delayed yolk sac resorption; hepatic Kupffer cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia (granuloma-like lesions) with abundant gram-negative bacilli can occur
- S. Typhimurium causes high mortality in passerines, young lories and African gray parrots
Laboratory Animals and Rodents Most commonly S. Typhimurium and S. Enteriditis; disease and outbreaks are rare now but may be common in the pet trade; hepatic, splenic and lymph node granulomatous inflammation and necrosis with “button ulcers” in the colon and segmental intestinal infarction due to mesenteric or mesocolic vascular thrombosis
- Gerbils: Causes diarrhea and up to 90% mortality in young gerbils 3-10 weeks old; disease is similar to that reported in other animals: enteritis and septicemia
- Guinea pigs: Discussed above
- Hamsters: Syrian hamsters are very susceptible; outbreaks are common in pet rodents including multidrug-resistant isolates resulting in zoonotic infections
- Mice: B6, C3H/HeJ, C57BL/10ScCr and BALB/c highly susceptible, A/J and CBA/N intermediate and 129S6/SvEv are resistant; Unlike infection in other animals, the alimentary tract is typically essentially normal, but systemic lesions are similar (e.g. paratyphoid nodules); Salmonella carriers are often intermittent shedders, so the highest rate of detection is achieved by culturing the mesenteric lymph node
- Rabbit: Can result in explosive epizootics of septicemia, abortion, and rapid death +/- diarrhea
- Rat: subclinical infections are frequent; ileum and cecum are distended with fluid feces with flecks of blood, +/- thickening of the affected intestine, +/- focal mucosal ulcerations, splenomegaly is common
- Chinchilla: S.Typhimurium resulted in septicemia (abortion, acute necrotizing hepatitis, splenitis, lymphadenitis, cystitis, pneumonia, enterocolitis, gastritis and/or nephritis) (Santos et al. 2022)
Nonhuman Primates
- Asymptomatic carriers are common; zoonotic and readily transmitted
- Serovars most commonly associated with enterocolitis are S. Typhimurium, and S. enteriditis
- Disease is similar to that in other species presenting often as mild, self-limiting illness that may cause severe diarrhea, sepsis, and death in neonates, elderly, debilitated, or immunocompromised animals and rarely results in septicemia
- Lesions may affect any region of the gastrointestinal tract but are most common in the ileum and colon; necrotizing and suppurative enterocolitis, pyogranulomatous hepatitis
- Salmonellosis in laboratory colonies is less common than Shigella sp. or Campylobacter sp.
- In apes, Salmonella spp. can cause acute hemorrhagic enterocolitis with septicemia in young, old, and immunocompromised individuals
Reptiles
- The most important zoonotic disease of reptile origin; clinical salmonellosis is rare in reptiles but asymptomatic carriers are common; cloacal swabs of asymptomatic reptiles is most accurate for detection (Fagre et. al. 2020)
- Clinical infection of snakes can result in emaciation, hepatitis, enterocolitis, myocarditis, pancreatitis, osteomyelitis, pericarditis, and splenitis (Bertolini et. al 2021)
- Snakes: S. arizonae in vertebral osteomyelitis, necrotizing alimentary tract lesions
Other Wildlife
- Elephants: enteritis, usually not septicemic unless immunosuppressed; S. Typhimurium, S. Dublin, S. Enteritidis
- Rhinoceros/tapir: Common cause of enteritis with septicemia including lung abscessation, fibrinous pleuritis, osteomyelitis
- Marsupials: Asymptomatic carriers; zoonosis
- Anteaters: Enteritis from contaminated feed or immunocompromise
- Cetaceans: S. Enterica isolated from the lung in both diseased and healthy porpoises
- Sirenia (manatees etc.): Gastroenteritis with septicemia
- Bats: Interstitial pneumonia and suppurative meningitis
- Penguins: S. Typhimurium and S. Anatis clinical enteritis, asymptomatic carriers
- Raptors: Isolated from normal and diseased raptors, sporadic disease similar to other avians
REFERENCES:
- Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ. Chapter 8: Hepatobiliary System. In: Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ, Barns HJ, eds. Avian Histopathology. 4th ed. Madison, WI: Omnipress; 2016: 358, 394-395.
- Agnew D, Nofs S, Delaney MA, Rothenburger JL. Xenartha, Erinacoemorpha, Some Afrotheria, and Phloidota. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:529.
- Barthold SW, Griffey SM, Percy DH. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits. 4th ed. Ames, IA: Blackwell Publishing; 2016: 58-59, 140, 184-185, 203, 228, 285.
- Bellido-Carreras N, Arguello H, Zaldivar-Lopez S, et. al. Salmonella typhimurium infection along the porcine gastrointestinal tract and associated lymphoid tissues. Vet Pathol. 2019;56(5):681-690.
- Bertolini M, Schwertz CI, Vielmo A, et. al. Pathological and microbiological findings in fatal cases of salmonellosis in captive Bothrops snakes in southern Brazil. J Comp Pathol. 2021; 186:7-12.
- Brady AG, Carville AAL. Digestive system diseases of nonhuman primates. In: Abee CR, Mansfield K, Tardiff S, Morris T, eds. Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research: Diseases, Vol. 2. 2nd ed. Waltham, MA: Academic Press; 2012:600-601.
- Clothier KA, Kim P, Mete A, Hill AE. Frequency, serotype distribution, and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Salmonella in small poultry flocks in California. J Vet Diag Invest. 2018;30(3):471-475.
- Costa RA, Casaux ML, Caffarena RD, et. al. Urocystitis and ureteritis in Holstein calves with septicaemia caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Dublin. J Comp Pathol. 2018;164: 32-36.
- Crespo R, Franca MS, Fenton H, Shivaprasad HL. Galliformes and Colubriformes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:759-760.
- Cullen JM, Stalker MJ. Liver and biliary system. In: Maxie MG, ed. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals. Vol 2. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:314-315.
- Delaney MA, Treuting PM, Rothenburger JL. Rodentia. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:509.
- Duncan M. Perissodactyls. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:448-449.
- Fagre AC, Pabilonia KL, Johnston MS, et. al. Comparison of detection methods for Salmonella enterica shedding among reptilian patients at a veterinary teaching hospital. J Vet Diag Invest. 2020;32(1):118-123.
- Farina LL, Lankton JS. Chiroptera. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:620.
- Fenton H, McManamon, Howerth EW. Anseriformes, Ciconiiformes, Charadriiformes, and Gruiformes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:711-712.
- Fulton RM. Bacterial diseases. In: Boulianne M., ed. Avian Disease Manual. 8th ed. Jacksonville, FL: American Association of Avian Pathologists; 2019:101-108.
- Grandolfo E, Parisi A, Ricci A, et. al. High mortality in foals associated with Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica Abortusequi infection in Italy. J Vet Diag Invest. 2018;30(3):483-485.
- Hensel M, Meason-Smith C, Plumlee QD, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Aetiological Agents Associated with Pulmonary Mycosis Secondary to Enteric Salmonellosis in Six Horses by Panfungal Polymerase Chain Reaction. J Comp Pathol. 2020;174:1-7.
- Higgins D, Rose K, Spratt D. Monotremes and Marsupials. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:471.
- Jones JL, Wang L, Ceric O, et. al. Whole genome sequencing confirms source of pathogens associated with bacterial foodborne illness in pets fed raw pet food. J Vet Diag Invest. 2019; 31(2):235-240.
- Landolfi JA, Terrell SP. Proboscidae. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:426-427.
- Lowenstine LJ, McManamon R, Terio KA. Apes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:395.
- Martinez MAJ, Gasper DJ, Mucino MCC, Terio KA. Suidae and Tayassuidae. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:218.
- Matz-Rensing K, Lowenstine LJ. New World and Old World Monkeys. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:357.
- Mendonça FS, Navarro MA, Uzal FA. The comparative pathology of enterocolitis caused by Clostridium perfringens type C, Clostridioides difficile, Paeniclostridium sordellii, Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Typhimurium, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in horses. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2022;34(3):412-420.
- Naberhaus SA, Krull AC, Bradner LK, et. al. Emergence of Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- as the primary serovar identified from swine clinical samples and development of a multiplex real-time PCR for improved Salmonella serovar level identification. J Vet Diag Invest. 2019;31(6):818-827.
- Origgi FC. Lacertilia. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:884.
- Ossiboff RJ. Serpentes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:904, 911.
- Owen H, Flint M, de Wilt M. Sirenia. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:600-601.
- Reavill DR, Dorrestein G. Psittacines, Coliiformes, Musophagiformes, Cuculiformes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:789.
- Riker J, Miller DM, Blas-Machado U, et al. Systemic salmonellosis in 4 cats. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2023;35(5):581-584.
- Rodriguez CE, Duque AMH, Steinberg J, Woodburn DB. Chelonia. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:843-844.
- Santos IR, Raiter J, Dal Pont TP, et al. Pathology of Salmonella enterica Subspecies enterica Serotype Typhimurium Infection in Chinchillas (Chinchilla lanigera). J Comp Pathol. 2022;194:14-21.
- Savic B, Zdravkovic N, Radanovic O, et. al. A Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Choleraesuis outbreak in weaned piglets in Serbia: clinical signs, pathologic changes, and microbiologic features. J Vet Diag Invest. 2021: 1-4.
- Schmidt R, Reavill DR, Phalen DN. Pathology of Pet and Aviary Birds. 2nd ed. Ames, IA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2015
- Shivaprasad HL. Chapter 11: Eye and Ear. In: Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ, Barns HJ, eds. Avian Histopathology. 4th ed. Madison, WI: Omnipress; 2016: 523, 526, 543.
- Siepker CL, Schwartz KJ, Feldhacker TJ, et al. Salmonella enterica serovar Brandenburg abortions in dairy cattle. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2022;34(5):864-869.
- Simmons J, Gibson S. Bacterial and mycotic diseases of nonhuman primates. In: Abee CR, Mansfield K, Tardiff S, Morris T, eds. Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research: Diseases, Vol. 2. 2nd ed. Waltham, MA: Academic Press; 2012:134-136.
- Spagnoli ST, Gelberg HB. Alimentary System and the Peritoneum, Omentum, Mesentery, and Peritoneal Cavity. In: Zachary JF, ed. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 7th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:396-485.
- St. Leger J, Raverty S, Mena A. Cetacea. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:558.
- Stanton JB, Zachary JF. Mechanisms of Microbial Infections. In: Zachary JF, ed. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 7th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:198-203.
- Stidworthy MF, Denk D. Sphenisciformes, Gaviiformes, Podicipediformes, Procellariiformes, and Pelecaniformes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:656.
- Swayne DE, Barnes HJ, Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ. Chapter 10: Nervous System. In: Abdul-Aziz T, Fletcher OJ, Barns HJ, eds. Avian Histopathology. 4th ed. Madison, WI: Omnipress; 2016: 477.
- Terio KA, McAloose D, Mitchell E. Felidae. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:277.
- Trupkiewicz J, Garner MM, Juan-Salles C. Passeriformes, Caprimulgiformes, Coraciiformes, Piciformes, Bucerotiformes, and Apodiformes. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:810.
- Uzal FA, Arroyo LG, Navarro MA, Gomez DE, Asín J, Henderson E. Bacterial and viral enterocolitis in horses: a review. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2022;34(3):354-375.
- Uzal FA, Plattner BL, Hostetter JM. Alimentary system. In: Maxie MG, ed. Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals. Vol 2. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:51, 99-100, 115, 167-176.
- Van Wettere AJ, Brown DL. Hepatobiliary System and Exocrine. In: Zachary JF, ed. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 7th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:515, 538.
- Welle MM, Linder KE. The Integument. In: Zachary JF, ed. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 7th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:1231.
- Wunschmann A, Armien AG, Hofle U, Kinne J, Lowenstine LL, Shivaprasad HL. Birds of Prey. In: Terio KA, McAloose D, St. Leger J, eds. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. London, UK: Academic Press; 2018:735-736.